Developed by
Center for Radiochemistry and Nuclear MaterialsDepartment of Chemistry
Loughborough University
Learning Goals
To measure the true activity of a heavily quenched 14C sample by the channels ratio method.Explanation and Exercise Guide
Theory
In liquid scintillation counting there are two forms of quenching, chemical and colour quenching. Chemical quenching is when a compound competes with the solute molecules (PPO, POPOP, dimethyl POPOP, etc.) for the excitation energy of the solvent. These quenching compounds absorb this energy but do not emit light when de-excited . Colour quenching is the partial absorption of the light produced by the solutes, thus reducing the light incident on the photo-cathode of the photomultiplier tube. This may occur to some extent if suspended material is present, but occurs to a larger extent in coloured solutions. The liquid scintillation counter acts as a spectrometer producing a beta spectrum. The result of quenching of either form effectively is to move the spectrum to lower energy (Figure 1).In liquid scintillation counting there are two forms of quenching, chemical and colour quenching. Chemical quenching is when a compound competes with the solute molecules (PPO, POPOP, dimethyl POPOP, etc.) for the excitation energy of the solvent. These quenching compounds absorb this energy but do not emit light when de-excited . Colour quenching is the partial absorption of the light produced by the solutes, thus reducing the light incident on the photo-cathode of the photomultiplier tube. This may occur to some extent if suspended material is present, but occurs to a larger extent in coloured solutions. The liquid scintillation counter acts as a spectrometer producing a beta spectrum. The result of quenching of either form effectively is to move the spectrum to lower energy (Figure 1).
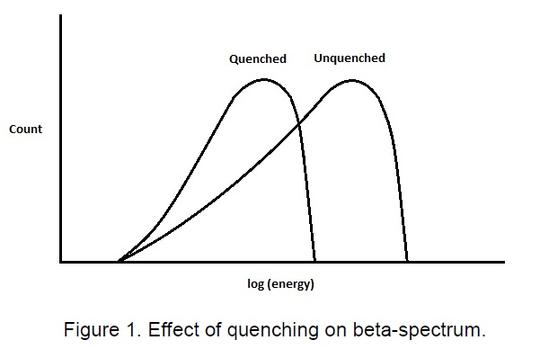
Whenever a series of samples is counted, either the efficiency and hence quenching must be constant, or the efficiency of counting must be determined for every sample. It is essential therefore to ascertain whether quenching is occurring and to correct for this when determining counter efficiency. There are, essentially, three main ways of correcting for quenching.
1. Internal Standard
A known amount of active material is added to all samples which are then recounted. A comparison of the activity is added, and the increase in count will enable the efficiency of counting to be calculated.
Efficiency = (Increase in count (cpm) / Total activity added (dpm) ) * 100%
2. External Standard
An external radioactive source, e.g. 137Cs is brought into a fixed position close to the liquid scintillation samples which are recounted. The increase in count rate can be used in calibration to indicate the efficiency of counting. This method is commonly used in automatic scintillation counters and often combined with method 3.
3. Channels Ratio Method (this experiment uses this method )
Since the effect of quenching is to move the beta spectrum to lower energies, if the spectrum is counted in two separate channels the ratio of the counts in the two channels will be a measure of the movement in the spectrum and hence an indication of the degree of quenching taking place (see figure 2.)

e.g. R = count in channel 1 / count in channels (1+2),
or R = count in channel 2/ count in channel 1 etc
All have valid applications for particular instruments and/or isotopes.
Experimental Procedure
Experimental procedure for quench corrections in liquid scintillation countingQuestions for the Students
What are the energies of channels 1 and 2?Why does the counting efficiency decrease as more quenching agent is added?
Other
Safety Aspects
- Disposable gloves and eye protection should be worn to avoid direct contact with the radioactive material and scintillation fluid.
- DO NOT dispose of any liquid or solid waste down sinks or in waste bins. Place in the red waste buckets provided.
- The addition of carbon tetrachloride should be carried out in a fume cupboard
Description of the equipment needed and used during the exercises.
Preparation for the lab Supervisor
EquipmentScintillation counter -14C
channel
10-200 μl Autopipette
Consumables
15 mL Scintillation fluid
Scintillation vials
200 μL Carbon tetrachloride
200 μL tips
Sources
15 mL 14C n-hexaecane in scintillation fluid @0.213 kBq per mL)
Standards 14C #107 & 3H #108